
(QuantumDesign, qdusa.com/products/ppms.html). Samples are mounted on 2.3 cm diameter pucks that are inserted into the measuring chamber by rods and connected at the bottom of the dewar to the measuring systems. Samples can be, depending on the property in question, in the form of solids, powders and thin films. Small sample sizes (1-500 mg) are in general needed and temperature sweeps can be made at rates 0.01-6 K/min.
Equipment at the department for preparation of samples for the PPMS include several blade saws, a wire saw and grinding/polishing machines.
Capabilities/Accessories
-
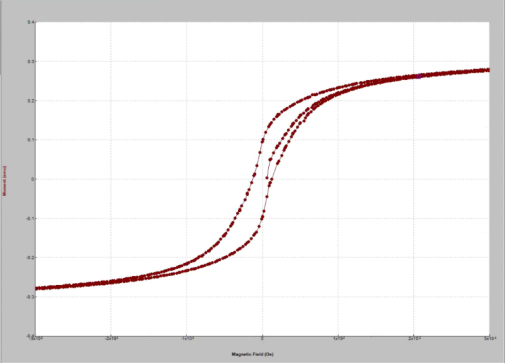
The basic magnetic measurement system provides for measurements of dc magnetization (M-H curves) for H up to 9 T and ac magnetization for fields 2 nOe-15 Oe and frequencies 10 Hz-10 kHz.
-
A 40 Hz vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) enables high sensitivity magnetic susceptibility measurements. The VSM comes with high temperature capability and magnetic susceptibility measurements may be performed to up to 1000 K in high vacuum.
-
The ac transport system has a precision current source and voltage detector that enables measurements of (i) dc and 1 Hz - 1 kHz ac resistivity (4-point and van der Pauw) in the range nΩ - kΩ, (ii) Hall effect, (iiii) I-V curves and (iv) super-conductor critical current and field.
-
The resistivity option adds a configurable resistance bridge board and enables measurements of dc and ac resistivity in the range Ω to MΩ.
-
The heat capacity system uses a two-tau model to remove the background heat capacity of the sample platform and has a resolution of 10 nJ/K at 2K.
-
The thermal transport system enables simultaneous measurements of (i) ac resistivity, (ii) thermal conductivity, (iii) Seebeck coefficient and (iv) figure-of-merit zT.
Example/Application areas
Hall coefficient

Thermal conductivity

Seebeck coefficient

Electric conductivity

Magnetic susceptibility

Magnetization versus field
Recharge rates: the current rate for using the PPMS is 1000 SEK/day for all users.



